Varicose veins, or varicose veins, in everyday life are often referred to as "the disease of tired legs". But in reality, the factors that cause it are much more complicated. And the disease itself is by no means just a harmless cosmetic defect. Varicose veins of the lower extremities lead to the occurrence of chronic venous insufficiency - a condition, the end result of which may be the onset of a venous trophic ulcer.
Of course, in the vast majority of cases these are varicose veins of moderate severity, which are now treated effectively and practically without relapse. But first the main things.
Why are varicose veins dangerous?
How common varicose vein disease is, it is difficult to say: many patients consider it a cosmetic defect and do not go to the doctor. According to Western scientists, at least a quarter of the population in the United States and Europe suffer from it. In our country, the disease has been registered in more than 30 million people. At the same time, according to some studies, no more than 18% are aware of their disease and no more than 8% receive treatment.
Varicose veins of the lower extremities are a disease in which the structure of the venous wall changes. The vessels stretch, twisted, in the areas of thinning of the walls, the lumen expands, forming nodes.
Statistics
Varicose veins are a disease with a hereditary predisposition. The probability of its occurrence in those in whose family no one has suffered from venous pathology is not more than 20%. If one of the parents is sick, the risk increases: for men - up to 25%, for women - up to 62%. In the presence of the disease in both parents, the probability of varicose veins in the offspring is 90%.
With varicose veins, the relationship between the two main structural proteins of the venous walls is disturbed:collagenAndelastin. . . If collagen forms stiffness, elastin, as the name suggests, is responsible for elasticity, the ability of the venous wall to return to its original state. In patients with varicose veins, the amount of this protein in the vein wall is reduced. The collagen itself also changes: instead of the prevailing type III collagen, which is responsible for elasticity, it increases the content of type I collagen - rigid, keeping the residual deformation. In addition, the number of smooth muscle cells that regulate the lumen of the vessel also changes, and the ability to interact with each other is impaired. These pathological changes are hereditary in nature. Then the game comes into playexternal factors:
- long-term static loads - the need to stand or sit still;
- overweight;
- pregnancy and childbirth.
Some experts point to chronic constipation, tight clothing that increases intra-abdominal pressure and high heels that interfere with the normal functioning of the muscle pump in the legs as predisposing factors.
Individually or in combination, these factors increase the pressure within the venous system of the lower extremities. The altered venous wall ceases to "hold" the pressure, the lumen of the vein expands. Due to the expansion of the lumen of the vein, the valves, which supply blood flow in only one direction, stop working. It risesreflux- reverse outflow. The pressure inside the affected vein increases even more and the vicious circle closes.
Increased venous pressure, combined with changes in the wall structure over time, triggerinflammatory response- initially only on the surface of the valves and on the inner wall of the vessels. Gradually, inflammatory proteins and blood cells begin to "seep" through the damaged vein wall into surrounding tissue. There they are destroyed, releasing active substances -inflammatory mediators. . . They damage the surrounding cells and attractlymphocyteswhose function is to remove damaged tissue. As a result, edema, hardening (hardening) of the skin of the legs and hyperpigmentation develop. These processes can cause venous trophic ulcers. Prolonged inflammation of the venous wall also increases blood clotting. In combination with venous congestion, this leads to the fact that blood clots begin to form in the varicose vein. It risesthrombophlebitis- another dangerous complication of varicose veins.
Manifestations of varicose veins are divided into objective and subjective.subjective symptoms- these are the patient's complaints about:
- heaviness in the legs;
- rapid fatigue;
- paraesthesia - unpleasant sensations of "goosebumps", changes in sensitivity;
- burning sensation in the muscles;
- pain in the legs, the feature of which is that the intensity decreases after a walk;
- swelling in the evening;
- restless legs syndrome - a condition in which discomfort in the legs prevents you from falling asleep;
- night cramps in the lower limbs.
The combination of these symptoms and their severity are individual and do not always correlate with changes in the venous wall and surrounding tissues.
The combination of subjective disorders and objective changes in the tissues of the lower extremities forms the basis of the modern classification of varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency:
- C0- there are complaints, but there are no changes in appearance, lesions of the veins can only be detected with a special examination and tests;
- do1- "spiders" appear (scientific name - telangiectasias) or a network of intradermal dilated veins (reticular varices) becomes visible;
- do2- the diameter of the dilated saphenous veins exceeds 3 mm, varicose nodes appear;
- C3- the affected leg becomes constantly swollen;
- C4- changes appear in the surrounding tissues: the skin darkens (hyperpigmentation), eczema develops, hardening of the subcutaneous tissue;
- C5- the stage of the healed ulcer;
- C6- the stage of an open ulcer.
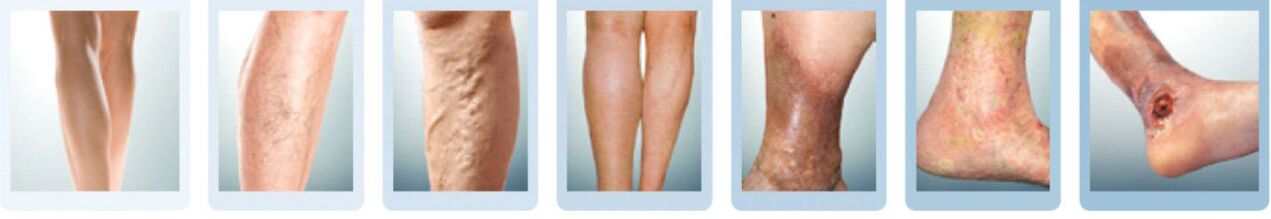
From the fourth stage, the trophic changes in the skin described can no longer be completely eliminated. Even varicose veins treated at this stage will not lead to complete resorption of hyperpigmentation or hardening. In addition, it is necessary to remember a rather dangerous complication:thromboembolism. . .
on a note
From 30 to 60% of deaths due to sudden onset deep vein thrombosis and further thromboembolism occur against the background of varicose veins in combination with undetected and not treated in time thrombophlebitis.
Therefore, you should not postpone the treatment of varicose veins until later, especially against the background of the achievements of modern phlebology.
Modern methods of treatment of varicose veins
Methods and techniques that meet several criteria can be considered modern: minimal invasiveness (trauma), high efficiency, low probability of relapses and complications and a short rehabilitation period.
- Conservative therapy.Includes the use of compression stockings, ointments and venotonics (oral medications). Current clinical guidelines suggest that venotonics can reducesubjectivemanifestations (complaints) in the early stages of the disease and reduce edema, but in no way affect the state of the venous wall itself. Different types of ointments have the same effect. Compression hosiery is considered a very effective treatment for varicose veins, as it reduces the manifestations of venous insufficiency, relieves the patient's subjective ailments and prevents the progression of varicose veins. However, compression stockings are unable to cure varicose veins - dilated veins will not function properly.
- Traditional surgical removal.The affected large or small saphenous vein is tied at the place where it flows into the deep venous system, after which it is removed with a special metal probe. This operation is effective, but rather traumatic and requires a long recovery. There is a high probability of postoperative complications: hematomas, postoperative paraesthesia and neuralgia.
- Sclerotherapy.A special drug is injected into the varicose vein, which "glues" its walls. The procedure is not very traumatic and is recommended for the treatment of small diameter veins. However, it is rarely used to remove the inoperative trunk of the large and small saphenous veins, as it is characterized by a higher recurrence rate. In addition, such an unpleasant complication as hyperpigmentation in the framework of sclerosis is possible.
- Intravenous laser coagulation (EVLK)- minimally invasive, safe, modern and effective type of varicose vein treatment. It has synonymous names: intravenous laser ablation, intravascular coagulation of the veins of the lower extremities, intravenous laser obliteration (EVLO). But whatever the name, the laser coagulation technique remains the same. A radial fiber optic light guide is inserted through the puncture into the vein. Then, with the help of a special pump, an anesthetic solution is pumped around the vein, which not only anesthetizes the procedure, but also compresses the vein, reducing its diameter and thus protecting the surrounding tissues from overheating. For the procedure, modern vascular lasers are used, which generate two waves: one of them is absorbed by the hemoglobin of the blood, the second by the vascular wall. Vienna is "beer". All phases (position of the light guide, infiltration of the solution around the vein, the "brewing" process itself) are monitored in real time by ultrasound devices. The duration of the EVLK procedure on one limb is 30-60 minutes.
It is important to know!
The only effective method of treating varicose veins is to remove the altered vein that is unable to perform its functions.
The advantages of the laser removal method:
- Minimal trauma, which allows the procedure to be performed on an outpatient basis and under local anesthesia;
- you can go home immediately after the operation;
- fast recovery;
- good aesthetic result: no marks and scars remain;
- high efficiency, low recurrence rate.
Since intravenous laser coagulation is currently considered one of the most advanced, low-traumatic and minimally invasive types of varicose vein treatment, we will consider this technique in more detail.
Indications for laser coagulation
The main indication is varicose veins, regardless of the diameter of the venous trunk and the options for its anatomical structure. EVLK's range of indications could be extended thanks to the perfection of modern equipment: two-wave lasers, radial fibers.
Contraindications to the procedure
In most cases, they boil down to severe somatic condition of the patient:
- deep vein thrombosis (obstruction, occlusion, block);
- decompensated type 1 diabetes mellitus;
- severe atherosclerosis of the arteries and ischemia of the lower extremities;
- severe cardiovascular diseases: ischemic heart disease, in particular angina pectoris at rest, extensive myocardial infarction with decreased cardiac output, severe forms of cardiac arrhythmias, stroke;
- severe blood clotting disorders, both downward and upward;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- individual intolerance to the anesthetic used;
- impossibility of physical activity immediately after the procedure;
- inability to use compression stockings.
It is characteristic that the patient's age is not a contraindication.
How is laser coagulation of the veins performed?
Shortly before manipulation, you should purchase compression stockings of the 2nd degree of compression (25-32 mm Hg). The doctor will tell you in detail which size is required. Intravascular laser coagulation by itself does not require any special preparation.
All stages of intravenous laser obliteration are performed under constant ultrasound control.
- Before the procedure begins, the vein is "marked": the doctor puts marks on the skin, corresponding to the points where the blood flows back, the tributaries flow into the vein.
- At the beginning of the manipulation, local anesthesia occurs, the vein is punctured (punctured). The sensations are no different from the usual intravenous injection. A radial light guide is inserted into the vein using a special catheter.
- A protective "sleeve" of the anesthetic drug is then created around the vein. Under ultrasound control, using a special pump, the doctor injects a local anesthetic into the space around the vessel. This allows not only to relieve pain, but also to protect the surrounding tissue from excess laser heat.
- The procedure itself is EVLO varicose veins. In modern optical fibers, laser radiation is delivered evenly over the entire circumference of the device, providing uniform heating of the vein from the inside. After removing the light guide, the patient undergoes ultrasound monitoring of the condition of the treated vessel, as well as the deep veins of the limb.
- A compression garment is put on the patient.
Immediately after the end of the manipulation, the patient should go for a walk, lasting at least 40 minutes.
Possible complications
There are few of them, they are temporary, and the likelihood of complications is mainly associated with the use of outdated medical equipment and the low qualifications of a doctor.
- Deep vein thrombosis -it may appear in patients with a tendency to increase thrombosis. Therefore, to prevent this complication, patients are prescribed drugs that reduce blood clotting. As a rule, they are used within 4-5 days after surgery.
- Thrombophlebitis- most often associated with insufficient intensity of laser exposure.
- Pigmentation along the treated veinresolves within 1. 5-2 months.
- Feeling of a "stretched" vein- passes within 1, 5 months.
In order to prevent the development of any complications as much as possible, it is necessary to adhere to a few simple rules, observance of which is necessary for successful rehabilitation.
rehabilitation
On the first day, there may be pulling aches and pains along the vein. To eliminate them, conventional painkillers are enough. The temperature may rise in the first few days. Just take the traditional means to reduce it.
In general, for successful rehabilitation, 2 main conditions must be observed: wearing compression underwear and maintaining sufficient physical activity.
- Compression underwear -during the first 5 days, it is not removed even during night sleep. This is necessary for the vein to be completely "glued" and healed. Also, compression stockings are only worn during the day. It is enough to wear compression clothing for 2. 5-3 months, but if there are risk factors (sedentary, standing work, taking female sex hormones), additional preventive wear of compression stockings is desirable.
- Physical activity- It is recommended to walk for at least one hour a day. But you will have to give up intensive sports for about a month.
During the month, you should avoid hot baths, baths and saunas.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the method
The analysis of foreign and domestic publications shows that the efficiency of laser coagulation of varicose veins varies from 93 to 100%. Failures can be attributed to several groups of factors:
- anatomical features of the operated vein;
- violations of the technical performance of EVLK (insufficient laser power, insufficient compression of the vein with an anesthetic solution);
- non-compliance by the patient with the rules of the postoperative regimen (usually - rejection of compression).
The immediate and long-term results of laser coagulation of the lower limb veins are better than those of radiofrequency ablation and sclerotherapy and are comparable to traditional surgical techniques. At the same time, the treatment of varicose veins with a laser is much better tolerated, the rehabilitation time is shorter, and the number of complications is less than in classic operations.
How much does EVLK cost?
The intravasal laser coagulation procedure requires high-tech equipment and expensive disposable consumables (light guides), which explains its cost. The total amount will depend on the volume and complexity of the procedure, the medical equipment used and the qualifications of the doctor.
Hence, intravenous laser coagulation is a modern effective method for the treatment of varicose veins. It gives excellent clinical results and, in fact, leaves no residue. The minimal trauma of exposure allows you to return to normal life (with minor restrictions) already on the day of surgery, without requiring a hospital regime and special conditions for recovery.
How to choose a clinic
Says a vascular surgeon, phlebologist:
"The result of laser coagulation of the veins of the lower limbs largely depends on the professionalism of the medical staff, as well as on the technical characteristics of the equipment used. This means that the equipment used must be modern and the doctors must be qualified. Therefore, I would recommend to choose a clinic specializing in this particular type of service, which has been operating for several years and has a proven reputation over time ".




































